Wine Basics with Food and Beverage Trainer
There are 5 main styles of wine
- Red Wine
- White Wine
- Rosé Wine
- Champagne/ Sparkling Wine
- Fortified Wine
There are many types of grapes that make many styles of wines for Red and White Wines
| WHITE WINE GRAPES | RED WINE GRAPES |
| Chardonnay | Shiraz |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Cabernet Merlot |
| Riesling | Cabernet Sauvignon |
| Semillon | Pinot Noir |
| Verdelho | Sangiovese |
| Chenin Blanc | Zinfandel |
| Pinot Gris or Pinot Grigio | Malbec |
When we talk about wines we describe the wines characteristics into the following
Categories;
- The Body
- The Texture
- The Aroma
- The Tannins
- The Acidity
| The Body | Full bodied wines tend to be rich & heavy in flavour & texture Light bodied wines tend to have a fresh watery flavour & texture Medium bodied wines are somewhere in between. Dry white wines tend to be full bodied – chardonnay & sauvignon blanc are examples of these. Desert wines are considered to be full bodied due to the amount of sugar inside. |
| The Texture | When we talk about the texture of a wine, we are essentially describing the mouth feel or tactile sensation on the palate frequently use when describing a wine’s texture are; creamy, smooth, rich, velvety, supple, fat, oily, waxy, juicy, silky, voluptuous and succulent |
| The Aroma | It is through smelling a wine that most of the flavor notes associated with wine are detected. Examples of most common aroma descriptors are; citrus, peach, melon, pomello, strawberry, blackberry, herbs, flowers, earth, grass, tobacco, butterscotch, toast, vanilla, mocha, and chocolate. |
| The Tannins | In wine, tannin is a textural element that makes wine taste dry Tannins are derived from the skins, stems and seeds of the grapes used to produce the wine. Wine tannins are most commonly found in red wine, although white wines have tannin from being aged in wooden barrels. Tannin tastes dry and you can feel it specifically on the middle of your tongue and the front part of your mouth and gums. |
| The Acidity | A wine’s acidity is what makes your mouth water after sipping . (Different to tannins that typically dry out your mouth after sipping) Acidity can be detected by the sharpness of the wine in the mouth, particularly around the edges of the tongue near the front. |
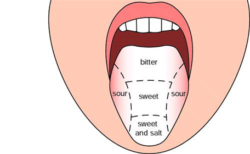
Tips For Pairing Wine & Food
- The wine should be more acidic than the food.
- The wine should be sweeter than the food.
- The wine should have the same flavour intensity as the food.
- Red wines pair best with bold flavoured meats (e.g. red meat).
- White wines pair best with light-intensity meats (e.g. fish or chicken).
- Bitter wines (e.g. red wines) are best balanced with fat.
- It is better to match the wine with the sauce than with the meat.
- More often than not, White, Sparkling and Rosé wines create contrasting pairings.
- More often than not, Red wines will create congruent pairings.

Check out this Food and Wine pairing Video @ Shoptopia – “6 Basic Rules for Pairing Food with Wine”
Train your staff with the wine basics with this ready made power point training
 | Training includes Lesson Plan PowerPoint Training (42 Slides) Quiz Roles Plays |
To purchase this training go Food and Beverage Trainings
References:
Tips for pairing food:
https://winefolly.com/wine-pairing/getting-started-with-food-and-wine-pairing/ accessed 12/01/2022
https://www.australianwine.com/en-AU/our-story/articles/5-steps-to-pairing-food-with-wine accessed 12/01/2022
| F&B Forms | Job Descriptions | SOP’s | Training Packages | Free Trainings |
